In collaboration with the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) under the Cooperating Technical Partners Program (read more…), EDAC created and manages the New Mexico Wildfire Risk Assessment Portal (NMWRAP). In an effort to increase wildfire awareness, NMWRAP is an interactive web map that allows users to view if they are at risk for wildfires in New Mexico. The web map also has tools for users to create maps, and download data and reports.
In July 2019, EDAC required a grant through the NARA’s NHPRC (National Archive and Records Administration’s National Historical Publications and Records Commission) to digitize historical aerial photos from 1934-1987. The photos are from New Mexico and nearby regions in neighboring states. Digitizing these photos included a process of scanning, georeferencing, creating metadata, indexing, archiving, and making them web-accessible.
An API was also created by the EDAC IT Team to georeference images and add metadata by users online. The software development is open source and the code is available here.
The project was finished in June 2022, with a grand total of 32,358 images digitized and free to download for the public. These photos can be accessed on historicalaerialphotos.org and RGIS.
The Earth Data Analysis Center provided data collection, data processing, and mapping support to the New Mexico Office of Secretary of State for carrying out work related to the Local Election Act (LEA), which was passed by the New Mexico Legislature in 2018. LEA provides for local elections to be held simultaneously throughout the state of New Mexico. Special voting district boundary data was collected from district contacts and/or their data stewards. The data was processed and made into digital format when necessary, or they can be viewed on the New Mexico Political Subdivisions Map. Voter addresses were standardized and geocoded. Overlay analyses were executed with voter address points, special voting district boundaries, and voting precinct boundaries to determine voter count per area. This work assists in the preparation for future local elections.

The New Mexico 911 (NM911) Program was created by Section 63-9D-1 through 63-9D-20 NMSA 1978 (“Enhanced 911 Act”) to further the public interest and protect the safety, health, and welfare of the people of New Mexico by enabling the development, installation, and operation of enhanced 911 emergency reporting systems to be operated under shared state and local government management and control. The New Mexico Department of Finance and Administration (NM DFA) manages the NM911 Program.
The NM911 Program administers essential emergency reporting and dispatch services accessible by calling nine-one-one through forty-one disparately funded municipal and county-run public safety answering points (PSAPs or 911 centers) located throughout the state.
In January 2019, The NM911 Program contracted with the Earth Data Analysis Center (EDAC) at the University of New Mexico (UNM) and Bohannan Huston, Inc. to securely acquire geospatial data from local government entities, validate and process data into the statewide model; and make such data available for download on the PSAP Map Servers. Earth Data Analysis Center is responsible for securely acquiring GIS data from primary GeoData Providers, verifying and validating data, processing to convert those to the statewide master dataset, generating assessment reports identifying errors or discrepancies per NM911 standards, and providing reports back to the GeoData providers. In addition, these data are updated on PSAP Map servers for emergency response. The road centerlines and address points (statewide) are available on NM RGIS Geospatial Data Clearinghouse as shapefiles for public access.
In order to aid in the protection of the dune sagebrush lizard (Sceloporus arenicolus) habitat, Natural Heritage New Mexico (NHNM) is collaborating with EDAC to map its range in detail. The lizard is found only on the shinoak (Quercus havardii) dunelands of southeastern New Mexico, comprising some 1,415,000 acres. As this habitat is a checkerboard of control of federal, state, and private land managers and faces an increasing number of threats from competing land uses, the need to know where important and viable habitat still exists is critical. So beginning in 2011, field crews from NHNM have gone out to the shinoak dunelands and collected and described land cover for a number of ground control plots. These plots have been used by EDAC in turn with multi-temporal Landsat imagery from 2011 as well as the NAIP 2011 digital ortho-photography to create a land cover map at a 1m spatial resolution which is intended to be useful to land managers at a 1:12,000 scale. The area was mapped into 18 different land cover classes, of which the most important is to separate the healthy shinoak dunelands and dune blowouts, which are critical to the survival of the lizard, from areas of disturbance and degraded habitat.
As part of an ongoing national program to inventory and map vegetation cover for all of the 280 park units in the United States, EDAC and Natural Heritage New Mexico (NHNM) developed a vegetation map for the 115,000-acre El Malpais National Monument located in western New Mexico. The rugged nature of the topography dominated by lava flows and volcanoes, some only a few thousand years old, made it especially challenging to gather field data and created much more reliance on the imagery to classify the area. Still, NHNM managed to collect some 476 ground plots from 2003 to 2009 which described the vegetation cover for a sample terrain of 400 m2. These ground data sets were then used by EDAC to create a classification from multi-temporal Landsat imagery and natural color digital ortho-photography. The spectral depth and seasonality of the Landsat imagery was used to model differences in surface reflectance and phenology between vegetation types whereas the photography was used to enhance the spatial resolution of the final product. The resulting map classified the park into 12 Map Unit Level 1 classes (equivalent to the NVCS Group level) and 49 Map Unit Level 2 classes (equivalent to the NVCS Alliance level). The completed maps and accompanying reports have been provided to the US National Park Service as digital products to aid in the present and future management of their natural resources.
FEMA’s Risk Mapping, Assessment, and Planning (RiskMAP) Program’s vision is to provide quality data that increases public awareness and leads to action that reduces risk to life and property. The New Mexico Department of Homeland Security (NMDHSEM) and Earth Data Analysis Center are working with FEMA Region VI as Cooperating Technical Partners through RiskMAP to prioritize flood-related data needs throughout the state. NMDSHEM and EDAC operate the NMFlood website that hosts interactive maps, current flood-related news, and links to online flooding tools and are active in the New Mexico Floodplain Managers Association and New Mexico Silver Jackets.
As a component of a larger NASA-funded project on the Integration of Airborne Dust Prediction Systems and Vegetation Phenology to Track Pollen for Asthma Alerts in Public Health Decision Support Systems, EDAC is developing a web-based decision support system for forecasting Juniperus ashei, Juniperus monosperma, Juniperus scopulorum, and Juniperus pinchotii pollen concentration data. Designed to meet the requirements of New Mexico’s Environmental Public Health Tracking System (NM EPHTS), the system includes state-of-the-art statistical analysis tools, geospatial visualization tools, data discovery, extraction, and delivery tools, and environmental/public health linkage information. Earth science data obtained from Earth observatories are ingested into the Pollen Regional Atmospheric Model (PREAM) by team members at the University of Arizona. EDAC receives output files from the model which then are run through a post-processing routine to develop products that are made available to NM EPHTS via web mapping and web coverage services.
New Mexico’s history of mining and exploration makes it home to hundreds of abandoned settlements. Intrepid research into the history of these settlements yielded a compilation of our state’s documented ghost towns. Here is a link to the interactive map.
The data used to create this map, which includes names, locations, and the condition of the ghost town, are available for download from RGIS.
The New Mexico Broadband Program (NMBB) began in 2010 as part of the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) State Broadband Initiative (SBI), which implemented the joint purposes of the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 and the Broadband Data Improvement Act. The SBI program facilitated the integration of broadband and information technology into state and local economies.
After that initiative was completed, EDAC continued working with the New Mexico Department of Information Technology (DoIT) on several other broadband projects, such as the Governor’s Broadband for Education Initiative, PSFA Broadband Deficiencies Correction Program (BDCP), and the NM Rural Broadband Project (RBBP). In 2022 the Office of Broadband Access and Expansion (OBAE) and the Connect New Mexico Fund (CNMF) were created. This later gave way to the Connect New Mexico Pilot Program (CNMPP), a grant program that allows awarded Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to bring broadband to unserved and underserved communities.
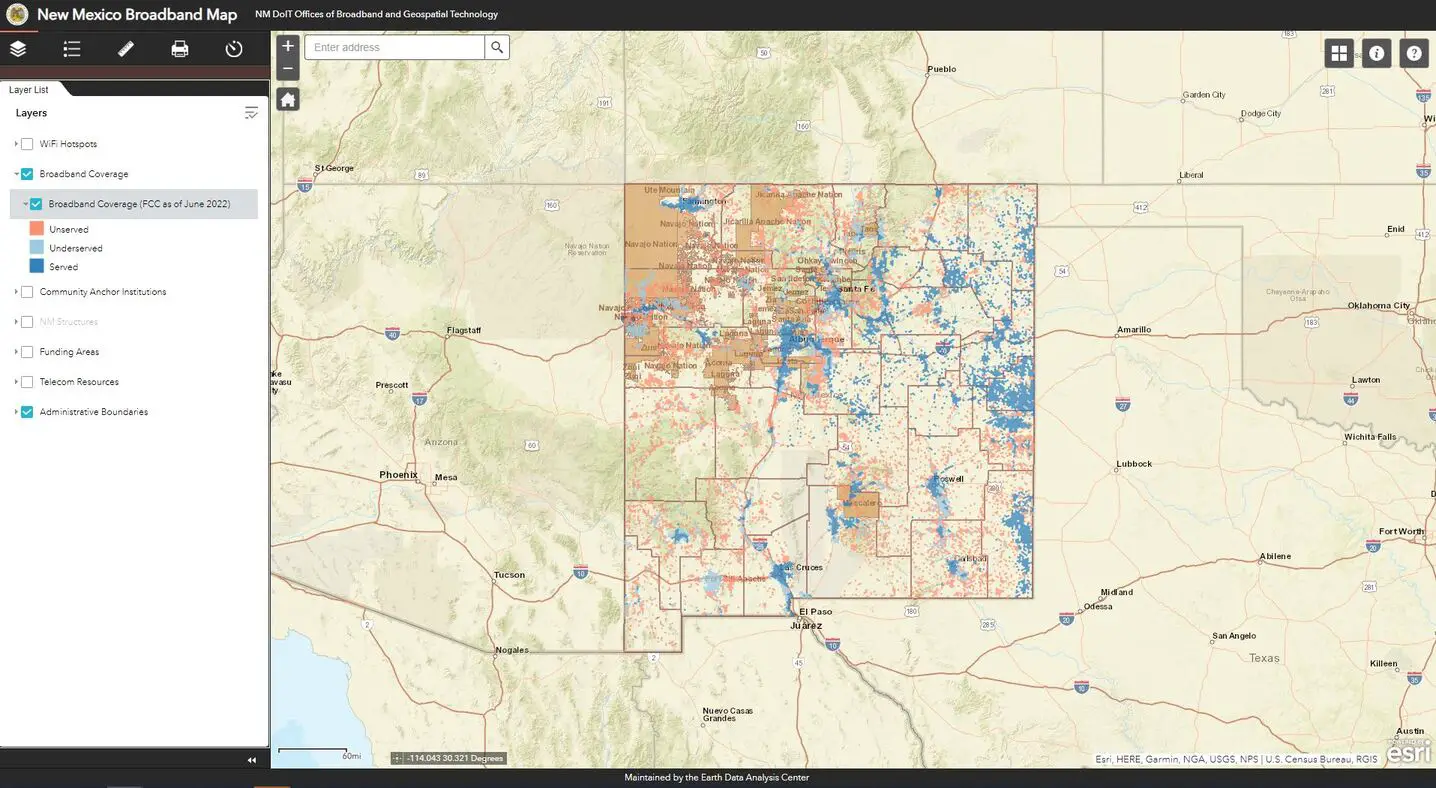
EDAC continues to maintain the New Mexico Broadband Map (NMBB Map), which had originally been created in partnership with DoIT for the NTIA SBI project. The NMBB Map, http://nmbbmapping.org/mapping/, is an interactive web map that displays broadband availability based on download/upload speeds: Served (100/20 Mbps or more), Underserved (from 25/3 Mbps to just under 100/20 Mbps), and Unserved (less than 25/3 Mbps). This data is derived from the Federal Communications Commission (FCC)’s Broadband Serviceable Locations (BSL) data. The NMBB Map also includes other relevant data: Community Anchor Institutions (CASA database), NM structures, funding areas, telecom resources, WiFi hotspots, and administrative boundaries for reference.
The map allows consumers to see broadband availability and policymakers to address the barriers for broadband expansion and to improve broadband adoption in underserved and unserved communities. The adoption of high-speed Internet services and information technology enhances economic development, public safety, health care, educational opportunities, and the quality of life for New Mexicans.
 EDAC attended the NM Department of Health kick-off for New Mexico’s Environmental Public Health Tracking (EPHT) Program in 2002 and has participated in the NM EPHT Program in the years since. New Mexico is an original Grantee in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) National Environmental Public Health Tracking Program and is currently one of 24 EPHT Grantees. This CDC program provides state health departments with resources to create statewide networks that integrate data sets, tools, and standards, thus allowing the state network to be an interoperable component of the National EPHT Network. New Mexico supports the national EPHT goals to prevent or reduce illnesses, injuries, and deaths related to environmental risk factors and to increase the understanding of the relationships between environmental exposures and health effects.
EDAC attended the NM Department of Health kick-off for New Mexico’s Environmental Public Health Tracking (EPHT) Program in 2002 and has participated in the NM EPHT Program in the years since. New Mexico is an original Grantee in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) National Environmental Public Health Tracking Program and is currently one of 24 EPHT Grantees. This CDC program provides state health departments with resources to create statewide networks that integrate data sets, tools, and standards, thus allowing the state network to be an interoperable component of the National EPHT Network. New Mexico supports the national EPHT goals to prevent or reduce illnesses, injuries, and deaths related to environmental risk factors and to increase the understanding of the relationships between environmental exposures and health effects.
EDAC develops, implements, and enhances the NM EPHT Network/System (NM Tracking) nmtracking.doh.nm.gov and its relevant data services. NM Tracking consists of a content management system for text- and graphics-based information and an interactive, dynamic data analysis, visualization, and reporting application. The portal provides a secured, publicly accessible, Web-based mechanism to exchange data and information between data stewards, analysts, and New Mexicans and the public; to discover and view data; and to explore relationships between environmental exposures and potential health outcomes. To achieve this, NM Tracking uses an online data registry to make environmental public health information, data, and standardized metadata available for query, visualization, download, and report generation. Data security is ensured through secure Internet transmissions, encrypted messaging, and authenticated and authorized user roles in all communications between NM Tracking and the NMDOH environmental health-data provider NM-IBIS and other distributed data providers.
This project is no longer active
The “New Mexico Watch – Active Wildfires” was a public website developed and hosted by the Earth Data Analysis Center that provided information about active wildfires in the state of New Mexico. NMWatch integrated local data (public schools, hospitals, fire stations, law enforcement, community centers, watershed boundaries) with active wildfire perimeter and location information generated daily by the Geospatial Multi-Agency Coordination Group (GeoMAC). Local fire information was added as available from NM Fire Info (New Mexico Fire Information). Users were able to measure distance and calculate area using built-in tools.
In 2010 and 2011 EDAC contracted with the New Mexico Office of the State Engineer to georectify several hundred historic water-related maps. The first project was to georectify hydrographic survey maps of the Pecos Basin using the 2005 statewide digital aerial imagery as the mapping base. Some of the maps date as far back as the 1920s. Following the completion of that project EDAC moved to the western side of the state to do a second map georectification project in the Gila / San Francisco Basin. These maps are called Proof of Beneficial Use (PBU) maps and are used in validating historical water use within the state. These maps were especially difficult to georectify because there was almost no control point information on the maps except for the PLSS section and quarter section corners. Because of that, we were unable to use a photo map base as was done in the Pecos Basin project. The best mapping base that could be found was the statewide PLSS shapefile and the digital raster graphic (DRG) mosaic of the USGS 1:24,000 map sheets.
From 2007 to 2011, EDAC, in conjunction with Natural Heritage New Mexico, mapped the land cover of the 7,000-acre Petroglyph National Monument. Although covering a relatively small area, the park with its volcanoes and lava cliffs found at the transition between the Great Plains, the Desert Basin, and the Chihuahuan Desert communities has a fair amount of diversity. The mapping process combined multi-temporal high and moderate spatial resolution satellite imagery and digital ortho-photos along with field plot data to create the map. The resulting map grouped several dozen vegetation communities identified at the park into some 25 separate land cover types ranging from barren lava rocklands to grasslands and shrublands. The resulting map provides the US Park Service with a data source to aid in their management of park resources and a baseline from which to compare future changes.
As part of a project being conducted by URS Corp to map the land-use change in Harris County, Texas (greater Houston), EDAC was contracted in 2011 to create an ortho-photo map of the county using aerial photography acquired in 1983. At that time the National High Altitude Program acquired some 117 color IR photos over the area. Photo transparencies were obtained from the USGS and scanned at 2,000 dpi. The scanned photos were then rectified to the most recent photo base map for the county while using USGS 10 m spatial resolution DEMs for the elevation values. The resulting ortho-photos were mosaicked together to create the 1983 ortho-photo map at 1m spatial resolution.
This project is no longer active
 The New Mexico Public Schools Facilities Authority (PSFA) Statewide Web map was developed to communicate information about public schools in the State of New Mexico. The Web Map displayed public school information including school enrollment numbers, school capacity calculations, the New Mexico Facilities Database ranking information, and community assets are presented in tabular and graphical formats.
The New Mexico Public Schools Facilities Authority (PSFA) Statewide Web map was developed to communicate information about public schools in the State of New Mexico. The Web Map displayed public school information including school enrollment numbers, school capacity calculations, the New Mexico Facilities Database ranking information, and community assets are presented in tabular and graphical formats.
At the beginning of almost every legislative session, EDAC provides representatives of New Mexico’s Senate and House Districts with maps depicting the locations of University of New Mexico (UNM) Students, Employees, and Alumni within the individual districts. According to Marc H. Saavedra, UNM’s Director of the Office of Government and Community Relations, “The legislators really appreciate having the map at the start of every legislative session. The map also plays a big role in making the legislature aware of how UNM is across the entire State and in their district.”
The Pre-Disaster Hazard Mitigation Act of 2010 (PDM), administered by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), provides funding and technical assistance to state and local governments for disaster preparedness and management. Over the last two years, UNM has developed the first university-approved Natural Hazard Pre-Disaster Mitigation Plan in New Mexico. The ongoing program aims to develop ways to reduce the impact of natural disasters on UNM’s resources by identifying natural hazards and associated risks applicable to UNM, determining the impacts of these hazards, setting mitigation goals, and developing strategies that would lessen potential impacts.
EDAC’s role in the plan is to perform a fundamental analysis of top hazards likely to affect UNM by identifying such as thunderstorms, lightning, hail, winter storms, extreme cold/heat, wind/dust storms, tornadoes, flooding, wildfires, drought, and earthquakes and by incorporating factors such as building age, building use, and building function to properly assess the risk associated with various hazards. Through output maps and reports, hazard awareness can be better understood and shared. Priorities then can be established and the mitigation plan implemented.
Because universities provide structure and stability to local economies and directly influence their surrounding communities, states, and local governments, having a Pre-Disaster Mitigation Plan that saves lives, reduces damage and monetary loss, and keeps universities’ doors open and fully operational is essential.
Started in 1999, the International Charter on Space and Major Disasters is a cooperative agreement between the world’s major space agencies to pool their remote sensing satellites and archival imagery libraries to aid countries whose people are impacted by natural or man-made disasters. When a disaster occurs the Charter members decide on what types of satellite imagery are appropriate, initiate new collections by the satellites, and open up their archives for historical imagery. The imagery is then obtained and delivered to first response officials on the ground at no charge to the end users. Should a Charter-eligible disaster strike New Mexico in the future, Paul Neville, GIS Specialist/Programmer, has been selected by the Charter members to be the state Project Manager. He would be in charge of receiving all imagery from the Charter members and delivering it to the local end users in whatever format is chosen.
Exposure to fine particulate dust and adhered endotoxins is an increasing Public Health concern, particularly in the exacerbation of cardiovascular and respiratory diseases. This concern is demonstrated by the deployment (funded by NASA’s REASoN program) of a moderate-resolution dust forecasting system (the DREAM ETA model) into the SYRIS syndromic surveillance system, and through ongoing interest by the NM Department of Health in the deployment of dust, pollen, and other environmental data sets into New Mexico’s Environmental Public Health Tracking Network (EPHTN). In support of these systems, more rapidly available and higher spatial resolution data are needed for more localized assessment of particulate exposure for use in epidemiological studies, and for more timely and targeted notification of dust events to at-risk populations.
Researchers at the University of New Mexico, George Mason University, and the University of Arizona had previously been funded by NASA to conduct an Interoperability Testbed project in 2007 to demonstrate key model and data interoperability capabilities of the Dust Regional Atmospheric Model (DREAM ETA); the higher particle- size resolution, 8-bin DREAM ETA model; and the higher spatial resolution DREAM NMM model.
This project builds upon our previous work in the Interoperability Testbed and the PHAiRS projects through two related activities to be undertaken by EDAC and our collaborators at George Mason University (funded by NASA through their 2008 Research Opportunities in Space and Earth Sciences NRA): 1) determining the feasibility of deploying a nested dust forecasting system that consists of initial low spatial resolution (8-bin DREAM ETA) model runs that identify regions for which an HPC-enabled, high-spatial-resolution DREAM NMM model should be run; and 2) developing an interoperable framework that uses OGC and W3C standards to enable model and data interoperability to streamline the execution of the model chain and deliver the products of the model runs into public health decision support systems such as EPHTN and SYRIS.
From 2001 to 2009, EDAC, in conjunction with Natural Heritage New Mexico, mapped the land cover of the 34,000-acre Bandelier National Monument in north-central New Mexico. The monument presented some unique challenges, from an elevation difference of 5,000 feet to a terrain that includes riverine and lacustrine habitats, deep incised canyons, and tall peaks capped by sub-alpine forests. In addition, throughout the project, the region underwent a significant ecological change as the ubiquitous pinyon woodlands suffered a near-total dieback. The mapping process combined multi-temporal, moderate spatial resolution satellite imagery with digital ortho-photos along with the field plot data to detect and classify the different mixes of plant cover types. The resulting map grouped the hundreds of separately identified vegetation communities found at the park into 70 separate land cover types. The resulting map provides the US Park Service with a data source to aid in their management of park resources and a baseline from which to compare future changes.
Beginning in 2005, EDAC in conjunction with Natural Heritage New Mexico mapped the land cover of the 86,000 acre Guadalupe Mountains National Park in western Texas. A diverse range of environments are found in the park from the gypsic dunes and alkali playas on the west side, to the oak scrubland on the east side, to the montane conifer forests in the peaks that rise 4,000 feet above the basin floor. The mapping process combined multi-temporal, moderate spatial resolution satellite imagery with digital ortho-photos along with field plot data to detect and classify the different mixes of plant cover types. The resulting map grouped the hundreds of separately identified vegetation communities found at the park into almost 70 separate land cover types. The resulting map provides the US Park Service with a data source to aid in their management of park resources and a baseline from which to compare future changes.
This project is no longer active
This three-year NASA-funded project was built upon EDAC’s combined experience and capabilities built as part of the PHAiRS and NM EPHT projects through the development of dust and ozone forecast products and information delivery capabilities that are deliverable through the NM EPHT system. This project delivered PM2.5 and PM10 raster and aggregated vector data products into the NM EPHT system, and through our past work with modelers at the University of Arizona and NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center delivered enhanced dust and ozone forecasts into NM EPHT.
Almost continuously since 1994, EDAC has provided the Cooperative Monitoring Center (CMC) at Sandia National Laboratories with technical assistance in remote sensing and GIS technology. The mission of the CMC is to demonstrate the various unclassified technologies that can be used in border monitoring, arms control, and international security. EDAC provides expertise in remote sensing and GIS by obtaining satellite imagery and other geospatial data for a variety of CMC international projects. We assist the CMC with border monitoring analyses, modeling, and imagery interpretation. The CMC has a visiting scholars program that hosts a wide range of domestic and international experts, and EDAC assists them with geospatial information and training. We also provide remote sensing presentations and demonstrations at CMC workshops and conferences. Presentations are conducted in Albuquerque, elsewhere domestically, and on occasion, internationally.
 EDAC, in collaboration with UNM’s Bureau of Business and Economic Research (BBER) and under contract to the NM Department of Finance and Administration, addressed the population undercount in the Local Update of Census Addresses (LUCA) Program used to update and improve the U. S. Bureau of Census Master Address File. EDAC used digital aerial imagery for interpreting and counting housing structures within 3,500 Census blocks. These blocks were selected to provide the greatest impact upon areas that are historically the most undercounted due, in large part, to the poor addressing found in these regions. Overall, the program provided an additional 131,283 housing units not previously identified by the Census Bureau enumeration. New Mexico may benefit by as much as $11 million per year in increased federal funding once these additions are accepted by the Census Bureau.
EDAC, in collaboration with UNM’s Bureau of Business and Economic Research (BBER) and under contract to the NM Department of Finance and Administration, addressed the population undercount in the Local Update of Census Addresses (LUCA) Program used to update and improve the U. S. Bureau of Census Master Address File. EDAC used digital aerial imagery for interpreting and counting housing structures within 3,500 Census blocks. These blocks were selected to provide the greatest impact upon areas that are historically the most undercounted due, in large part, to the poor addressing found in these regions. Overall, the program provided an additional 131,283 housing units not previously identified by the Census Bureau enumeration. New Mexico may benefit by as much as $11 million per year in increased federal funding once these additions are accepted by the Census Bureau.
 EDAC, in cooperation with the New Mexico Department of Homeland Security and Emergency Management (DHSEM), continues the partnership among state and Federal agencies, local communities, tribal entities, and professional associations to assess, inventory, acquire, and distribute data that support coordinating, planning, and developing floodplain mapping, as stated in New Mexico’s Map Modernization Management Support (MMMS) business plan. EDAC provides the State with an ongoing coordinated floodplain mapping program. In light of the Flood Map Modernization Mid-Course Adjustment, greater focus has been placed on compliance with FEMA’s 2005 Floodplain Boundary Standard, which includes providing access to the most current and accurate digital data layers. The digital data will be accessible to engineers, local communities, and citizens of New Mexico thus providing officials information required for accurate assessment of risk-based mapping priorities.
EDAC, in cooperation with the New Mexico Department of Homeland Security and Emergency Management (DHSEM), continues the partnership among state and Federal agencies, local communities, tribal entities, and professional associations to assess, inventory, acquire, and distribute data that support coordinating, planning, and developing floodplain mapping, as stated in New Mexico’s Map Modernization Management Support (MMMS) business plan. EDAC provides the State with an ongoing coordinated floodplain mapping program. In light of the Flood Map Modernization Mid-Course Adjustment, greater focus has been placed on compliance with FEMA’s 2005 Floodplain Boundary Standard, which includes providing access to the most current and accurate digital data layers. The digital data will be accessible to engineers, local communities, and citizens of New Mexico thus providing officials information required for accurate assessment of risk-based mapping priorities.
 In 2008, the five-year NASA-funded REASoN project known as PHAiRS entered its fifth and final year. This project is unique in that it has successfully modified a dust forecast model for conditions in the southwest United States and improved the model’s performance by using NASA Earth observation data as input parameters. Furthermore, it has engaged the public health communities in Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas in all phases of the project. Significant progress has been made in developing a demonstration web client, the standards-based service-based architecture on which it depends, and the incorporation of EPA in-situ particulate matter concentration data. Most significant is the availability of forecast dust data via Open Geospatial Consortium web services, allowing users to quickly acquire data using time-enabled WMS requests, both through direct requests and through an online KML generation tool for streamlined visualization in desktop virtual globe applications such as Google Earth. In the final months of the project, the PHAiRS capabilities and products will be incorporated into the Syndrome Reporting and Information System (SYRIS) and tested by the City of Lubbock Department of Health and the Texas Department of Health District 1.
In 2008, the five-year NASA-funded REASoN project known as PHAiRS entered its fifth and final year. This project is unique in that it has successfully modified a dust forecast model for conditions in the southwest United States and improved the model’s performance by using NASA Earth observation data as input parameters. Furthermore, it has engaged the public health communities in Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas in all phases of the project. Significant progress has been made in developing a demonstration web client, the standards-based service-based architecture on which it depends, and the incorporation of EPA in-situ particulate matter concentration data. Most significant is the availability of forecast dust data via Open Geospatial Consortium web services, allowing users to quickly acquire data using time-enabled WMS requests, both through direct requests and through an online KML generation tool for streamlined visualization in desktop virtual globe applications such as Google Earth. In the final months of the project, the PHAiRS capabilities and products will be incorporated into the Syndrome Reporting and Information System (SYRIS) and tested by the City of Lubbock Department of Health and the Texas Department of Health District 1.
Demonstration Movies: